Middleware System
Fastay's middleware system provides a powerful way to intercept and process HTTP requests before they reach your route handlers. Middleware functions can perform tasks like authentication, logging, data validation, request transformation, and more.
What is Middleware?
Middleware is software that sits between the client request and your route handlers. It can:
- Inspect incoming requests
- Modify requests and responses
- Execute code before/after route handlers
- Terminate the request-response cycle
- Pass control to the next middleware or route handler
Think of middleware as a series of checkpoints that requests must pass through before reaching their destination.
How Middleware Works in Fastay
The Middleware Chain
When a request hits your Fastay application, it goes through a pipeline of middleware functions before reaching your route handler:
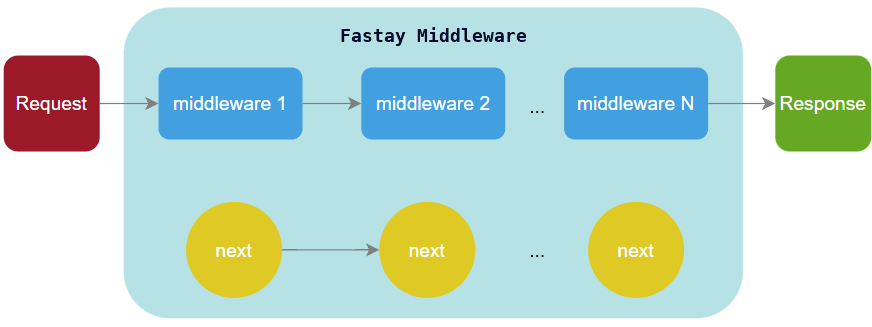
Each middleware function receives three parameters:
request: The HTTP request objectresponse: The HTTP response objectnext: A function to pass control to the next middleware
Middleware Execution Flow
- Request arrives at the server
- Middleware 1 processes the request (or modifies response)
- Middleware 1 calls
next()to pass to Middleware 2 - This continues until the Route Handler is reached
- The Route Handler sends the final response
- Response flows back through middleware in reverse order (if they modify responses)
Creating Your First Middleware
Basic Middleware Structure
Let's create a simple logging middleware:
// src/middlewares/logger.ts
import { Request, Response, Next } from "@syntay/fastay";
export async function logger(request: Request, response: Response, next: Next) {
// Record the start time
const startTime = Date.now();
// Log request details
console.log(
`${request.method} ${
request.path
} - Received at ${new Date().toISOString()}`
);
// Hook into when the response is finished
response.on("finish", () => {
const duration = Date.now() - startTime;
const statusCode = response.statusCode;
console.log(
`${request.method} ${request.path} - ${statusCode} - ${duration}ms`
);
});
// Pass control to the next middleware or route
next();
}
What this middleware does:
- Records the request start time
- Logs when a request arrives
- Sets up an event listener for when the response is sent
- Logs the request duration and status code when complete
- Calls
next()to continue processing
Applying Middleware to Routes
Middlewares need to be registered in Fastay's middleware configuration file:
// src/middlewares/middleware.ts
import { createMiddleware } from "@syntay/fastay";
import { logger } from "./logger";
import { auth } from "./auth";
export const middleware = createMiddleware({
// Apply logger to ALL routes
"/": [logger],
// Apply auth middleware only to specific routes
"/api/admin": [auth],
"/api/users": [auth],
// Apply multiple middlewares to a route (executed in order)
"/api/secure": [logger, auth, validation],
});
Key points about middleware registration:
- Use
"/"to apply middleware to all routes - Route paths are relative to your
baseRouteconfiguration - Middlewares execute in the order they're defined in the array
- You can apply different middleware combinations to different routes
Core Middleware Concepts
The Three Middleware Parameters
Every middleware function receives these three parameters:
export async function myMiddleware(
request: Request,
response: Response,
next: Next
) {
// 1. REQUEST OBJECT: Contains all information about the incoming request
console.log("Method:", request.method); // GET, POST, etc.
console.log("URL:", request.url); // /api/users?page=2
console.log("Headers:", request.headers); // All HTTP headers
console.log("IP Address:", request.ip); // Client IP address
console.log("Path:", request.path); // /api/users
console.log("Query:", request.query); // { page: "2" }
console.log("Params:", request.params); // Dynamic route parameters
console.log("Body:", await request.body); // Request body (JSON, FormData, etc.)
// 2. RESPONSE OBJECT: Allows modifying the response
response.setHeader("X-Custom-Header", "value");
response.status(201); // Set HTTP status code
// 3. NEXT FUNCTION: Passes control to the next middleware
next(); // Continue to next middleware or route handler
}
The next() Function
The next() function is crucial in middleware. It controls the flow of execution:
export async function middleware(
request: Request,
response: Response,
next: Next
) {
// Option 1: Continue normally
next(); // Passes control to next middleware/route
// Option 2: Skip remaining middleware and go directly to route
next("route"); // Only works in certain scenarios
// Option 3: Pass an error to error-handling middleware
next(new Error("Something went wrong")); // Triggers error handler
// Option 4: End the request-response cycle
// Don't call next() if you're sending a response
response.status(401).json({ error: "Unauthorized" });
// No next() call here - request stops
}
Fastay Middleware Patterns
Middleware in Fastay acts as a pipeline that processes HTTP requests before they reach your route handlers. They're perfect for cross-cutting concerns like authentication, validation, rate limiting, and CORS.
Authentication Middleware
This middleware secures routes by verifying JSON Web Tokens (JWT) and ensuring users are authenticated and active.
// src/middlewares/auth.ts
import { Request, Response, Next } from "@syntay/fastay";
export async function auth(request: Request, response: Response, next: Next) {
try {
// 1. Get token from Authorization header
const authHeader = request.headers.authorization;
if (!authHeader || !authHeader.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
return response.status(401).json({
error: "No authentication token provided",
code: "NO_TOKEN",
});
}
// 2. Extract and verify token
const token = authHeader.substring(7); // Remove "Bearer "
const decoded = verifyJwtToken(token);
// 3. Check if token is valid
if (!decoded) {
return response.status(401).json({
error: "Invalid or expired token",
code: "INVALID_TOKEN",
});
}
// 4. Check if user exists and is active
const user = await database.users.findUnique({
where: { id: decoded.userId },
});
if (!user) {
return response.status(401).json({
error: "User not found",
code: "USER_NOT_FOUND",
});
}
if (!user.isActive) {
return response.status(403).json({
error: "User account is deactivated",
code: "ACCOUNT_DEACTIVATED",
});
}
// 5. Attach user to request for use in routes
request.user = user;
// 6. Continue to next middleware or route
next();
} catch (error) {
// Handle unexpected errors
console.error("Auth middleware error:", error);
response.status(500).json({
error: "Authentication failed",
code: "AUTH_ERROR",
});
}
}
How It Works:
- Token Extraction: Checks the
Authorizationheader for a Bearer token - Token Validation: Verifies the JWT signature and expiration
- User Verification: Ensures the user exists and is active in the database
- Request Augmentation: Attaches the authenticated user to the
requestobject - Flow Control: Calls
next()to continue the request chain or returns an error response
Usage in Routes:
Once applied, the authenticated user becomes available in route handlers:
// src/api/admin/dashboard/route.ts
import { Request } from "@syntay/fastay";
export async function GET(request: Request) {
// The auth middleware attached user data to the request
const currentUser = request.user;
return {
message: `Welcome, ${currentUser.name}!`,
role: currentUser.role,
permissions: currentUser.permissions,
};
}
Request Validation Middleware
This middleware validates incoming request data using Zod schemas, ensuring data integrity before processing.
// src/middlewares/validate.ts
import { Request, Response, Next } from "@syntay/fastay";
import { z } from "zod";
// Define validation schemas
const userSchema = z.object({
name: z.string().min(2).max(100),
email: z.string().email(),
age: z.number().min(0).max(120).optional(),
});
export function validate(schema: z.ZodSchema) {
return async function (request: Request, response: Response, next: Next) {
try {
// Validate request body
const validatedData = schema.parse(await request.body);
// Replace request body with validated data
request.validatedBody = validatedData;
next();
} catch (error) {
if (error instanceof z.ZodError) {
return response.status(400).json({
error: "Validation failed",
details: error.errors.map((err) => ({
field: err.path.join("."),
message: err.message,
})),
code: "VALIDATION_ERROR",
});
}
// Pass other errors to error handling middleware
next(error);
}
};
}
// Create specific validation middlewares
export const validateUser = validate(userSchema);
export const validateProduct = validate(productSchema);
How It Works:
- Schema Definition: Uses Zod to define validation rules for data structures
- Request Parsing: Extracts and parses the request body
- Validation: Applies the schema to validate and coerce data
- Data Attachment: Stores validated data in
request.validatedBody - Error Handling: Returns detailed validation errors with field-specific messages
Usage:
// In middleware.ts
import { validateUser } from "./validate";
export const middleware = createMiddleware({
"/api/users": [validateUser],
});
// In route handler
export async function POST(request: Request) {
// Access validated data
const userData = request.validatedBody;
// No need for additional validation here
const user = await database.users.create({
data: userData,
});
return { user };
}
Rate Limiting Middleware
Protects your API from abuse by limiting the number of requests a client can make within a time window.
// src/middlewares/rateLimit.ts
import { Request, Response, Next } from "@syntay/fastay";
// Simple in-memory store (use Redis in production)
const requestCounts = new Map<string, { count: number; resetTime: number }>();
export function rateLimit(options: {
windowMs: number; // Time window in milliseconds
maxRequests: number; // Max requests per window
keyGenerator?: (req: Request) => string; // Custom key for grouping
}) {
return async function (request: Request, response: Response, next: Next) {
// Generate a unique key for this client (IP + optional user ID)
const key = options.keyGenerator
? options.keyGenerator(request)
: `${request.ip}:${request.path}`;
const now = Date.now();
const windowMs = options.windowMs;
const maxRequests = options.maxRequests;
// Get or create rate limit record for this key
let record = requestCounts.get(key);
if (!record || now > record.resetTime) {
// First request in this window or window has expired
record = {
count: 1,
resetTime: now + windowMs,
};
requestCounts.set(key, record);
// Set rate limit headers
response.setHeader("X-RateLimit-Limit", maxRequests.toString());
response.setHeader("X-RateLimit-Remaining", (maxRequests - 1).toString());
response.setHeader(
"X-RateLimit-Reset",
Math.ceil(record.resetTime / 1000).toString()
);
next();
} else if (record.count < maxRequests) {
// Increment count within the window
record.count++;
requestCounts.set(key, record);
// Update headers
response.setHeader("X-RateLimit-Limit", maxRequests.toString());
response.setHeader(
"X-RateLimit-Remaining",
(maxRequests - record.count).toString()
);
response.setHeader(
"X-RateLimit-Reset",
Math.ceil(record.resetTime / 1000).toString()
);
next();
} else {
// Rate limit exceeded
const retryAfter = Math.ceil((record.resetTime - now) / 1000);
response.setHeader("Retry-After", retryAfter.toString());
response.status(429).json({
error: "Too many requests",
message: `Rate limit exceeded. Try again in ${retryAfter} seconds.`,
code: "RATE_LIMIT_EXCEEDED",
retryAfter,
});
}
// Clean up old records periodically
if (Math.random() < 0.01) {
// 1% chance on each request
for (const [oldKey, oldRecord] of requestCounts.entries()) {
if (now > oldRecord.resetTime) {
requestCounts.delete(oldKey);
}
}
}
};
}
// Pre-configured rate limiters
export const apiRateLimit = rateLimit({
windowMs: 60 * 1000, // 1 minute
maxRequests: 100, // 100 requests per minute
});
export const authRateLimit = rateLimit({
windowMs: 15 * 60 * 1000, // 15 minutes
maxRequests: 5, // 5 attempts per 15 minutes
keyGenerator: (req) => `${req.ip}:auth`, // Group all auth attempts
});
How It Works:
- Client Identification: Creates a unique key for each client (IP + path or custom logic)
- Request Counting: Tracks request counts within configurable time windows
- Limit Enforcement: Blocks requests when limits are exceeded
- Header Information: Provides rate limit information via response headers
- Memory Management: Periodically cleans up expired records
Key Features:
- Informative Headers: Includes
X-RateLimit-Limit,X-RateLimit-Remaining, andX-RateLimit-Reset - Configurable Windows: Set different limits per endpoint or use case
- 429 Responses: Returns standard "Too Many Requests" status with retry information
- Production Ready: Designed to be extended with Redis for distributed systems
CORS Middleware
Enables Cross-Origin Resource Sharing, allowing controlled access to your API from different origins.
// src/middlewares/cors.ts
import { Request, Response, Next } from "@syntay/fastay";
export function cors(options: {
origin?: string | string[] | boolean;
methods?: string[];
allowedHeaders?: string[];
exposedHeaders?: string[];
credentials?: boolean;
maxAge?: number;
}) {
return async function (request: Request, response: Response, next: Next) {
// Handle preflight requests (OPTIONS method)
if (request.method === "OPTIONS") {
// Set CORS headers
if (options.origin) {
const origin = request.headers.origin;
if (options.origin === true) {
// Allow any origin
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", origin || "*");
} else if (Array.isArray(options.origin)) {
// Allow specific origins
if (origin && options.origin.includes(origin)) {
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", origin);
}
} else if (typeof options.origin === "string") {
// Allow single origin
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", options.origin);
}
}
// Set other CORS headers
if (options.methods) {
response.setHeader(
"Access-Control-Allow-Methods",
options.methods.join(", ")
);
}
if (options.allowedHeaders) {
response.setHeader(
"Access-Control-Allow-Headers",
options.allowedHeaders.join(", ")
);
}
if (options.exposedHeaders) {
response.setHeader(
"Access-Control-Expose-Headers",
options.exposedHeaders.join(", ")
);
}
if (options.credentials) {
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials", "true");
}
if (options.maxAge) {
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Max-Age", options.maxAge.toString());
}
// End preflight request
return response.status(204).end();
}
// For regular requests, set CORS headers
if (options.origin) {
const origin = request.headers.origin;
if (options.origin === true) {
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", origin || "*");
} else if (Array.isArray(options.origin)) {
if (origin && options.origin.includes(origin)) {
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", origin);
}
} else if (typeof options.origin === "string") {
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", options.origin);
}
}
if (options.credentials) {
response.setHeader("Access-Control-Allow-Credentials", "true");
}
next();
};
}
// Pre-configured CORS middleware
export const developmentCors = cors({
origin: true, // Allow any origin in development
credentials: true,
methods: ["GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE", "PATCH", "OPTIONS"],
allowedHeaders: ["Content-Type", "Authorization"],
});
export const productionCors = cors({
origin: ["https://example.com", "https://app.example.com"],
credentials: true,
methods: ["GET", "POST", "PUT", "DELETE"],
allowedHeaders: ["Content-Type", "Authorization"],
});
How It Works:
- Preflight Handling: Responds to OPTIONS requests with allowed methods and headers
- Origin Control: Validates requesting origins against allowed list
- Header Management: Configures which headers can be sent and exposed
- Credential Support: Enables cookies and authentication headers when needed
- Cache Optimization: Uses
Access-Control-Max-Ageto cache preflight responses
Key Features:
- Flexible Origin Configuration: Support for single origin, multiple origins, or wildcard (
true) - Preflight Optimization: Reduces overhead by caching preflight responses
- Security Focused: Restricts methods, headers, and credentials as needed
- Environment-Specific: Different configurations for development vs production
Middleware Configuration
Global Middleware vs Route-Specific Middleware
Fastay supports two types of middleware configuration:
1. Route-Specific Middleware (Recommended)
Configured in src/middlewares/middleware.ts:
// src/middlewares/middleware.ts
import { createMiddleware } from "@syntay/fastay";
import { logger } from "./logger";
import { auth } from "./auth";
import { cors } from "./cors";
import { rateLimit } from "./rateLimit";
export const middleware = createMiddleware({
// Apply to all routes
"*": [logger, cors],
// Apply to specific routes
"/api/auth/login": [rateLimit],
"/api/auth/register": [rateLimit],
// Apply multiple middlewares to a route
"/api/admin/*": [auth, adminOnly],
// Apply to nested routes
"/api/users": [auth],
"/api/users/*": [auth],
// Public routes (no auth required)
"/api/public/*": [],
"/api/health": [],
});
2. Global Middleware via Express Options
Configured in src/index.ts:
// src/index.ts
import { createApp } from "@syntay/fastay";
import helmet from "helmet";
import compression from "compression";
void (async () => {
await createApp({
port: 5000,
apiDir: "./src/api",
baseRoute: "/api",
expressOptions: {
middlewares: [
// These run for EVERY request, before route-specific middleware
helmet(), // Security headers
compression(), // Response compression
express.json(), // JSON body parser
express.urlencoded({ extended: true }), // URL-encoded body parser
],
},
});
})();
Middleware Execution Order
Middleware executes in this specific order:
- Global Express middlewares (from
expressOptions) - Route-specific Fastay middlewares (from
middleware.ts) - Route handler (your
route.tsfile)
Example with specific routes:
export const middleware = createMiddleware({
"/api/orders": [
cors, // 1. First: Set CORS headers
logger, // 2. Second: Log the request
auth, // 3. Third: Check authentication
validateOrder, // 4. Fourth: Validate request data
],
});
Advanced Middleware Patterns
Conditional Middleware
// src/middlewares/conditionalAuth.ts
import { Request, Response, Next } from "@syntay/fastay";
export function optionalAuth(request: Request, response: Response, next: Next) {
// Try to authenticate if token exists
const authHeader = request.headers.authorization;
if (authHeader?.startsWith("Bearer ")) {
const token = authHeader.substring(7);
try {
const decoded = verifyJwtToken(token);
request.user = await database.users.findUnique({
where: { id: decoded.userId },
});
} catch (error) {
// Token is invalid, but that's OK for optional auth
console.debug("Optional auth failed:", error.message);
}
}
// Always continue (user may be undefined)
next();
}
Usage:
// Some endpoints work with or without authentication
export const middleware = createMiddleware({
"/api/public-data": [optionalAuth],
});
// In route handler:
export async function GET(request: Request) {
if (request.user) {
// Return personalized data for authenticated users
return { personalized: true, data: getPersonalizedData(request.user) };
} else {
// Return generic data for anonymous users
return { personalized: false, data: getGenericData() };
}
}
Request/Response Transformation Middleware
// src/middlewares/transform.ts
import { Request, Response, Next } from "@syntay/fastay";
export function snakeToCamel(request: Request, response: Response, next: Next) {
// Transform request body keys from snake_case to camelCase
const originalJson = response.json;
response.json = function (data: any) {
if (data && typeof data === "object") {
data = transformKeys(data, (key) => {
return key.replace(/_([a-z])/g, (_, letter) => letter.toUpperCase());
});
}
return originalJson.call(this, data);
};
next();
}
// Helper function to recursively transform keys
function transformKeys(obj: any, transform: (key: string) => string): any {
if (Array.isArray(obj)) {
return obj.map((item) => transformKeys(item, transform));
}
if (obj && typeof obj === "object") {
const result: any = {};
for (const [key, value] of Object.entries(obj)) {
const newKey = transform(key);
result[newKey] = transformKeys(value, transform);
}
return result;
}
return obj;
}
Performance Monitoring Middleware
// src/middlewares/performance.ts
import { Request, Response, Next } from "@syntay/fastay";
import { performance } from "perf_hooks";
export function performanceMonitor(
request: Request,
response: Response,
next: Next
) {
const startTime = performance.now();
// Hook into response finish
response.on("finish", () => {
const duration = performance.now() - startTime;
// Log slow requests
if (duration > 1000) {
// 1 second
console.warn(
`Slow request detected: ${request.method} ${
request.path
} took ${duration.toFixed(2)}ms`
);
}
// Send metrics to monitoring service
sendMetrics({
method: request.method,
path: request.path,
statusCode: response.statusCode,
duration,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
});
});
next();
}
Cache Middleware
// src/middlewares/cache.ts
import { Request, Response, Next } from "@syntay/fastay";
// Simple in-memory cache (use Redis for production)
const cache = new Map<string, { data: any; expiry: number }>();
export function cacheMiddleware(options: {
ttl: number; // Time to live in milliseconds
keyGenerator?: (req: Request) => string;
skipCache?: (req: Request) => boolean;
}) {
return async function (request: Request, response: Response, next: Next) {
// Only cache GET requests
if (request.method !== "GET") {
return next();
}
// Skip cache if configured
if (options.skipCache && options.skipCache(request)) {
return next();
}
// Generate cache key
const cacheKey = options.keyGenerator
? options.keyGenerator(request)
: `${request.method}:${request.path}:${JSON.stringify(request.query)}`;
// Check cache
const cached = cache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached && cached.expiry > Date.now()) {
// Cache hit - return cached response
return response.json(cached.data);
}
// Cache miss - intercept the response
const originalJson = response.json;
response.json = function (data: any) {
// Store in cache
cache.set(cacheKey, {
data,
expiry: Date.now() + options.ttl,
});
// Clean old cache entries
cleanupCache();
return originalJson.call(this, data);
};
next();
};
}
function cleanupCache() {
const now = Date.now();
for (const [key, entry] of cache.entries()) {
if (entry.expiry < now) {
cache.delete(key);
}
}
}
// Usage
export const shortCache = cacheMiddleware({
ttl: 60 * 1000, // 1 minute
skipCache: (req) => req.path.includes("/no-cache/"),
});
Error Handling in Middleware
Error-Handling Middleware
Error-handling middleware has a different signature - it accepts four parameters:
// src/middlewares/errorHandler.ts
import { Request, Response, Next } from "@syntay/fastay";
export async function errorHandler(
error: Error,
request: Request,
response: Response,
next: Next
) {
console.error("Unhandled error:", {
message: error.message,
stack: error.stack,
path: request.path,
method: request.method,
timestamp: new Date().toISOString(),
});
// Handle different types of errors
if (error.name === "ValidationError") {
return response.status(400).json({
error: "Validation failed",
details: error.message,
code: "VALIDATION_ERROR",
});
}
if (error.name === "UnauthorizedError") {
return response.status(401).json({
error: "Authentication required",
code: "UNAUTHORIZED",
});
}
if (error.name === "ForbiddenError") {
return response.status(403).json({
error: "Insufficient permissions",
code: "FORBIDDEN",
});
}
if (error.name === "NotFoundError") {
return response.status(404).json({
error: "Resource not found",
code: "NOT_FOUND",
});
}
// Default to 500 Internal Server Error
const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV === "production";
response.status(500).json({
error: "Internal server error",
...(isProduction ? {} : { message: error.message, stack: error.stack }),
});
}
Registering error-handling middleware:
// Error handlers should be registered globally in expressOptions
await createApp({
expressOptions: {
middlewares: [
// Regular middlewares...
],
errorHandler: errorHandler, // Register your error handler
},
});
Passing Errors to Error Handler
You can pass errors to the error-handling middleware using next(error):
// In any middleware
export async function auth(request: Request, response: Response, next: Next) {
try {
// Authentication logic...
} catch (error) {
// Pass error to error-handling middleware
next(error);
}
}
Best Practices
Keep Middleware Focused
Each middleware should have a single responsibility:
// ✗ BAD: Multiple responsibilities
export async function doEverything(
request: Request,
response: Response,
next: Next
) {
// Authentication
// Logging
// Validation
// Rate limiting
// Compression
// etc.
}
// ✓ GOOD: Single responsibility
export async function logger(request: Request, response: Response, next: Next) {
// Only logs
next();
}
export async function auth(request: Request, response: Response, next: Next) {
// Only authentication
next();
}
Handle Errors Properly
Always handle errors in middleware and pass them along:
export async function middleware(
request: Request,
response: Response,
next: Next
) {
try {
// Your middleware logic
next();
} catch (error) {
// Don't swallow errors
next(error);
}
}
3. Consider Performance
Middleware adds overhead. Consider:
- Order matters: Put frequently failing checks (like auth) early
- Skip when possible: Use route-specific middleware instead of global
- Cache expensive operations: Like JWT verification or database lookups
- Use async appropriately: Only make middleware async if you need await
4. Test Your Middleware
Test middleware in isolation:
// test/middlewares/auth.test.ts
import { auth } from "../../src/middlewares/auth";
describe("Auth Middleware", () => {
it("should allow requests with valid token", async () => {
const mockRequest = {
headers: { authorization: "Bearer valid-token" },
};
const mockResponse = { status: jest.fn(), json: jest.fn() };
const mockNext = jest.fn();
await auth(mockRequest, mockResponse, mockNext);
expect(mockNext).toHaveBeenCalled();
});
it("should reject requests without token", async () => {
const mockRequest = { headers: {} };
const mockResponse = {
status: jest.fn().mockReturnThis(),
json: jest.fn(),
};
const mockNext = jest.fn();
await auth(mockRequest, mockResponse, mockNext);
expect(mockResponse.status).toHaveBeenCalledWith(401);
expect(mockNext).not.toHaveBeenCalled();
});
});
5. Document Your Middleware
Add JSDoc comments to your middleware:
/**
* Authentication middleware for Fastay
*
* @description
* Verifies JWT tokens from the Authorization header and attaches
* user data to the request object.
*
* @example
* // Apply to routes in middleware.ts
* export const middleware = createMiddleware({
* "/api/secure": [auth]
* });
*
* @param {Request} request - Fastay request object
* @param {Response} response - Fastay response object
* @param {Next} next - Next middleware function
* @throws {Error} If authentication fails
*/
export async function auth(request: Request, response: Response, next: Next) {
// Implementation...
}
Common Issues and Solutions
Middleware Not Executing
Problem: Your middleware isn't running for certain routes.
Solution:
- Check route patterns in
middleware.ts(they're case-sensitive) - Verify middleware is registered in the correct order
- Ensure you're not sending a response before middleware runs
Headers Already Sent
Problem: You get "Cannot set headers after they are sent to the client" error.
Solution:
- Don't call
next()after sending a response - Ensure only one middleware sends the final response
- Use return statements after sending responses
// ❌ BAD: Sending response AND calling next()
response.status(401).json({ error: "Unauthorized" });
next(); // Error: Headers already sent
// ✅ GOOD: Return after sending response
response.status(401).json({ error: "Unauthorized" });
return; // No next() call
Async/Await Issues
Problem: Middleware doesn't wait for async operations.
Solution:
- Make middleware async if it uses await
- Handle promises properly
// ✗ BAD: Promise not awaited
export function middleware(request: Request, response: Response, next: Next) {
database.query().then(() => {
next();
});
// Execution continues immediately
}
// ✓ GOOD: Async/await
export async function middleware(
request: Request,
response: Response,
next: Next
) {
await database.query();
next();
}
Real-World Example: Complete Authentication Flow
Here's a complete example of middleware for a real application:
// src/middlewares/middleware.ts
import { createMiddleware } from "@syntay/fastay";
import { logger } from "./logger";
import { auth, optionalAuth } from "./auth";
import { rateLimit } from "./rateLimit";
import { validateUser, validateLogin } from "./validate";
import { cors } from "./cors";
export const middleware = createMiddleware({
// Global middlewares
"/": [
logger,
cors({
origin:
process.env.NODE_ENV === "production" ? ["https://example.com"] : true,
credentials: true,
}),
],
// Public API endpoints
"/api/auth/login": [
rateLimit({ windowMs: 15 * 60 * 1000, maxRequests: 5 }),
validateLogin,
],
"/api/auth/register": [
rateLimit({ windowMs: 60 * 60 * 1000, maxRequests: 3 }),
validateUser,
],
// Protected endpoints
"/api/users": [auth],
"/api/users/": [auth],
"/api/posts": [optionalAuth], // Works with or without auth
"/api/posts/": [optionalAuth],
// Admin-only endpoints
"/api/admin/": [auth, adminOnly],
// Public endpoints (no auth needed)
"/api/public/": [],
"/api/health": [],
});
This comprehensive middleware system gives you complete control over your request processing pipeline, allowing you to build secure, performant, and maintainable APIs with Fastay.